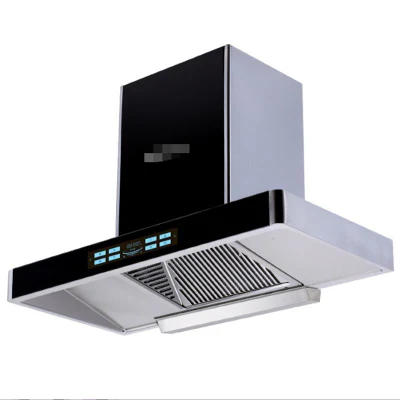
Heat Resistant Explosion Proof Laboratory Chemical Fume Hood with Acid & Alkali Resistant
Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | WJ-1800A |
| Feature | Corrosion Resistance, Heat Resistant, Acid & Alkali Resistant, Fireproof, Explosion Proof |
| Hood Type | Standard |
| Color | Grey |
| Customized | Customized |
| Condition | New |
| Input Power | 380V/50A |
| Application | Environment/Institute/Biology Lab/Chemical Lab |
| Face Velocity | 0.4-0.6 M/S |
| Worktop | 20+6 mm Ceramic |
| Liner Material | Ceramic Fiber Board |
| Product Name | Laboratory Fume Hood |
| Transport Package | Standard Export Wooden Case Packing |
| Specification | 1800*1205*2400 MM |
| Trademark | Ample |
| Origin | Chengdu, China |
| HS Code | 8414809090 |
| Production Capacity | 200 Set/Month |
Packaging & Delivery
Package Size 1900.00cm * 900.00cm * 2100.00cm Package Gross Weight 500.000kgProduct Description
Product Description
Now as the hood sash opens and closes, the hood's exhaust volumetric flow is varied as a linear function of the sash opening percentage (which is an indication of the hood face velocity).
Typically, there is a minimum flow that takes precedence when the sash is below 20% open. This relationship between the maximum and minimum flows is called the turndown ratio; for example if the maximum flow is 500 cfm and the minimum is 100 cfm, and the supply air is offset by 100 cfm, then the turndown ration required is 400:100 cfm, or 4:1.
This maintains a constant face velocity into the opening of the hood. A constant face velocity is a key element in successful hood control. Typical set points of acceptable face velocities range from 60 to 120 fpm. A maximum of plus/minus 5% set point control should be maintained at all times. Unstable or excess velocities can cause adverse effects, such as loss of containment, turbulence, eddy currents, glass breakage, blow out of heat candles, and leakage from the hood. The control system should have less than 1s response timings.
| Model Specification | WJ-1500A | WJ-1500B | WJ-1800A | WJ-1800B |
| External dimensions of equipment(mm) | 1500(W)*1205 (D) *2400 (H) | 1800(W)*1205 (D) *2400 (H) | ||
| Dimension of works pace (mm) | 1260(W1)*780(D1) *1100 (H1) | 1560(W1)*780(D1) *1100 (H1) | ||
| Panel material | 20+6mm thick butterfly ceramics | |||
| Material of internal lining board | 5mm thick ceramic fiber board | |||
| Diversion structure | Lower air return | |||
| Control system | Button control panel (LCD panel) | |||
| PH value control | The medium is alkaline water solution; manual monitoring, and manual control through acid pump and alkali pump. | |||
| Input power | Three-phase five-wire 380V/50A | |||
| Current for air fan | Not over 2.8A(380V or 220V can be directly connected) | |||
| Maximum load of socket | 12 KW(total of 4 sockets) | |||
| Water tap | 1 set (remote control valve + water nozzle) | No | 1 set (remote control valve + water nozzle) | No |
| Water discharge way | Magnetic chemical pump strong discharge | |||
| Using environment | For non-explosion indoor use, within 0-40 degrees Celsius. | |||
| Applicable fields | Inorganic chemistry experiment; Food, medicine, electronics, environment, metallurgy, mining, etc. | |||
| Ways of Purification | Spray sodium hydroxide solution, no less than 8 cubic meters/hour | Spray sodium hydroxide solution.no less than 12 cubic meters/ hour | ||
| Ways of surface air speed control | Manual control (through the electric air valve to adjust the exhaust air volume or adjust the height of the moving door) | |||
| Average surface air speed | 0.6-0.8 m/s Exhaust air volume: 1420-1890m3/h (when door height h =500mm) | 0.6-0.8 m/s Exhaust air volume: 1760-2340m3/h (when door height h =500mm) | ||
| Speed deviation of surface air | Not higher than 10% | |||
| The average intensity of illumination | Not less than 700 Lux; Standard white and uv-free yellow LED lamps; The illumination is adjustable. | |||
| Noise | Within 55 decibels | |||
| Flow display | White smoke can pass through the exhaust outlet, no overflow. | |||
| Safety inspection | No spikes, edges; Charged body and the exposed metal resistance is greater than 2 mQ; Under 1500V voltage, no breakdown or flashover occurred for 1min test. | |||
| Resistance of exhaust cabinet | Less than 160 pa | |||
| Power consumption | Less than 1.0kw/h (excluding power consumption of fans and external instruments) | Less than 1.2kw/h (excluding power consumption of fans and external instruments) | ||
| Water consumption | Less than 3.2L/ h | Less than 4.0L/ h | ||
| Performance of wind compensation | With a unique wind compensation structure, the volume of the wind will not cause turbulence in exhaust cabinet and will not directly blow to the staff (need to connect to the air compensation system of the laboratory) | |||
| Air volume regulating valve | 315mm diameter flanged type anti-corrosion electric air flow regulating valve (electric contact actuator) | |||
Fume hoods are typically used in laboratories to collect and exhaust fumes. The cross-section of a hood below has a vertical sash which can be raised and lowered as necessary. The horizontal air velocity into the hood is, typically, maintained at a constant velocity of 80-100 fpm whatever the sash height.
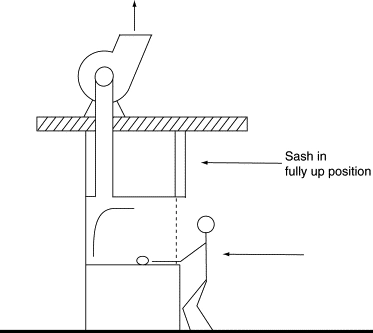
When the hoods are not operating, the room control is much the same as a normal occupancy for a variable air volume controlled room. When the hoods are operating, the control system senses the flows and pressures in the room, hoods, and ducts in and out, and makes adjustments to maintain the temperature, humidity, and pressurization of the room. The objectives for control in laboratory hoods are for the capture and containment of fumes and harmful gases, to maintain acceptable room pressurization, to maintain acceptable temperature and humidity set points, and to ventilate the space in order to preserve dilution of contaminants.
Many conditions can affect performance and speed of response from the control system. There are great cost differences between desired levels of control for these systems; the designer needs to know and account for the accuracy and reliability of controls required for the process.Detailed Photos
Fume Hood Maintenance
• Hoods should be evaluated by the user before each use to ensure adequate face velocities and the absence of excessive turbulence.
• In case of exhaust system failure while using a hood, shut off all services and accessories and lower the sash completely. Leave the area immediately.• Fume hoods should be certified, at least annually, to ensure they are operating safely. Typical tests include face velocity measurements, smoke tests and tracer gas containment. Tracer gas containment tests are especially crucial, as studies have shown that face velocity is not a good predictor of fume hood leakage.
• Laboratory fume hoods are one of the most important used and abused hazard control devices. We should understand that the combined use of safety glasses, protective gloves, laboratory smocks, good safety practices, and laboratory fume hoods are very important elements in protecting us from a potentially hazardous exposure.
• Laboratory fume hoods only protect users when they are used properly and are working correctly. A fume hood is designed to protect the user and room occupants from exposure to vapors, aerosols, toxic materials, odorous, and other harmful substances. A secondary purpose is to serve as a protective shield when working with potentially explosive or highly reactive materials. This is accomplished by lowering the hood sash.FAQ
6 Questions to Ask When Buying a Fume Hood:
-Which chemicals will you use within the hood?
-Is a ducted or ductless hood best suited to your needs and available space?
-Where will you place the fume hood in the lab? Consider workflows, access to external exhaust systems, and competing air patterns.
-What size fume hood will best suit your needs? Be sure to consider what (if any) equipment will be enclosed in the hood.
-Are any service fixtures or accessories such as airflow monitors, electrical outlets, water, or gas fixtures required?
-Are base cabinets for acid, solvent, or non-chemical storage required?
Prev: Hospital Pharmaceutical Laminar Flow Hood Laboratory Stainless Steel Laminar Flow Workbench
Next: Corrosion Resistance Acid & Alkali Resistant Laboratory Chemical Fume Hood with Heat Resistant
Our Contact






